
They are just the file versions of printf() and scanf(). Here, fptr is a file pointer associated with the file to be closed.įor reading and writing to a text file, we use the functions fprintf() and fscanf(). The file (both text and binary) should be closed after reading/writing.Ĭlosing a file is performed using the fclose() function. Open for both reading and appending in binary mode. Open for both reading and writing in binary mode. If the file does not exist, it will be created. If the file exists, its contents are overwritten. If the file does not exist, fopen() returns NULL. The reading mode only allows you to read the file, you cannot write into the file. The second function opens the existing file for reading in binary mode 'rb'.

This declaration is needed for communication between the file and the program. When working with files, you need to declare a pointer of type file.
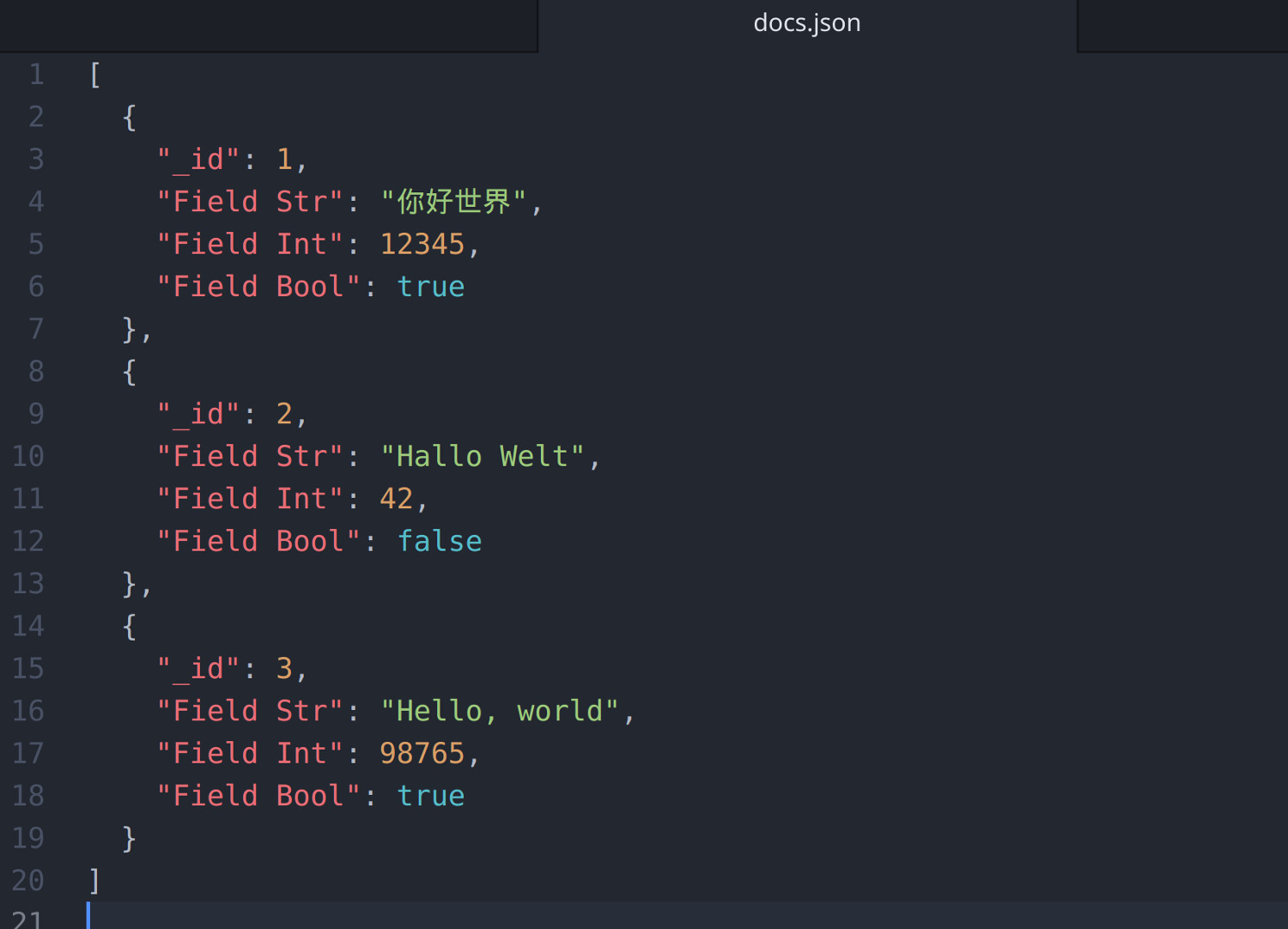
When you open those files, you'll see all the contents within the file as plain text. You can easily create text files using any simple text editors such as Notepad. When dealing with files, there are two types of files you should know about: You can easily move your data from one computer to another without any changes.However, if you have a file containing all the data, you can easily access the contents of the file using a few commands in C.
If you have to enter a large number of data, it will take a lot of time to enter them all.Storing in a file will preserve your data even if the program terminates. When a program is terminated, the entire data is lost.A file is a container in computer storage devices used for storing data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
